AC vs DC - for renewable energies, the difference between AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current) lies in their respective suitability for different stages of the energy generation, transmission, and consumption process.
Renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower, generate DC electricity which needs to be converted to AC for transmission over long distances, as AC electricity can be transmitted more efficiently than DC.
On the consumption side, AC is the standard for most household and commercial appliances, but some devices, such as electric vehicles, may use DC.
In summary, DC is more appropriate for localized generation and storage, while AC is better suited for long-distance transmission and widespread use.
Is the energy of renewable energy projects remunerated on an AC or DC basis?
The energy generated by renewable energy projects is generally remunerated on an AC basis. This is because the electrical grid, which is used to transmit and distribute the electricity, operates on AC. When the renewable energy source generates DC electricity, it is typically converted to AC before it is fed into the grid. Therefore, when the energy is sold to the grid operator, it is sold in AC form.
In some cases, the grid operator may require that the renewable energy source generate AC electricity directly, without conversion from DC. This depends on the specific regulations and requirements of each grid and country. However, in most cases, the energy of renewable energy projects is remunerated on an AC basis.

What is the purpose of inverters for renewable energy projects?
Inverters play a crucial role in renewable energy projects by converting DC (Direct Current) electricity generated by the renewable source, such as solar panels or wind turbines, into AC (Alternating Current) electricity that is compatible with the electrical grid and can be used by homes, businesses, and industry.
The purpose of inverters in renewable energy projects is to ensure that the electricity generated by the renewable source can be seamlessly integrated into the electrical grid and used in the same way as electricity from traditional sources. This makes renewable energy more practical and economically viable, as it enables the electricity generated by renewable sources to be sold to the grid and used by customers.
Inverters also play an important role in maintaining the quality of the electricity being fed into the grid, by regulating the voltage and frequency of the AC electricity generated by the renewable source. This helps to prevent power outages, surges, and other issues that could impact the stability and reliability of the electrical grid.
What is the purpose of an MMRA?
A Major Maintenance Reserve Account (MMRA) is a cash account established for the purpose of setting aside funds for future maintenance and repair costs for a specific asset or system. In the context of renewable energy projects, the MMRA is commonly used to set aside funds for the maintenance and repair of inverters.
Inverters play a crucial role in converting the DC electricity generated by the renewable energy source into AC electricity that is compatible with the electrical grid. Over time, the inverters may need to be repaired or replaced due to normal wear and tear, equipment failure, or other factors. The MMRA helps to ensure that the funds are available to pay for these costs when they arise rather than requiring a large, unexpected expense to be incurred all at once.
Having an MMRA helps to provide stability and predictability to the finances of the renewable energy project, as the funds are set aside in advance rather than being taken from other operating expenses or incurring additional funding.
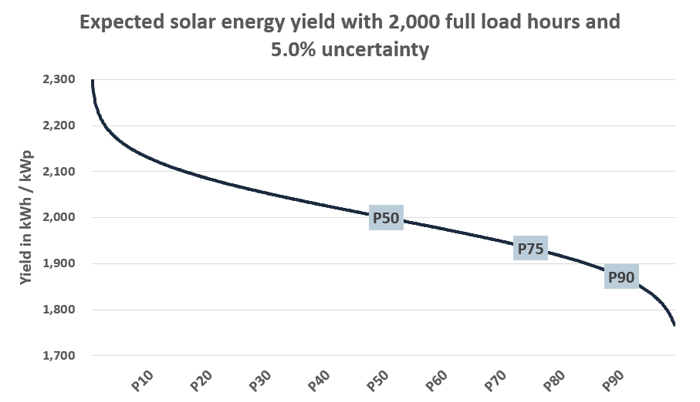
Is there a difference in the P50 production due to AC or DC?
The choice between AC and DC does not significantly influence the P50 production of a renewable energy asset. P50 production refers to the median or expected energy output of a renewable energy asset over a given time period, assuming normal weather conditions and proper functioning of the equipment.
Whether the energy is generated and transmitted in AC vs. DC form, the P50 production of the renewable energy asset will largely be determined by the characteristics of the energy source itself, such as its capacity and efficiency, as well as the weather conditions influence its energy output. For example, the P50 production of a solar panel will be largely determined by the amount of sunlight it receives, while the P50 production of a wind turbine will be determined by the wind speed and direction.
While the choice between AC vs. DC can impact the efficiency of the energy transmission and distribution system, it does not have a significant impact on the P50 production of the renewable energy asset itself.
How to build an advanced financial model for renewable energy investments?
Do you want to learn how to build a financial model created explicitly for renewable energy investments? Then check out the Advanced Renewable Energy Financial Modeling course.